Bass Tuba, brief description
“The tuba is currently used in four tunings: the bass tuba in F and Eb, and the contrabass tuba in C and Bb. In Austrian and French orchestras tubas in F and Bb are used, the contrabass tuba in Bb being found primarily in opera orchestras. In some regions of Germany and in Scandinavia, the United Kingdom and the USA the C tuba with four valves is common as a kind of all-round instrument: it is played not only in the orchestra but also in chamber music and as a solo instrument.”
Contrabass Tuba, brief description
“The contrabass tuba is currently made in two tunings: C and Bb. It is used primarily in opera orchestras and in brass and military bands. It is rarely asked for in symphony orchestras. Contrabass tubas are basically made in two different forms: the tuba form and the spiral form. Spiral tubas are also known as helicons.”
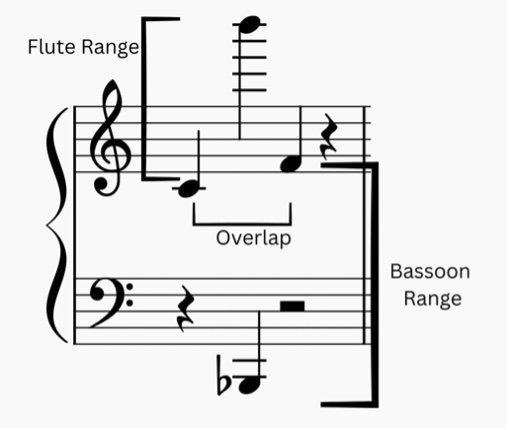
Flute, brief description — Vienna Symphonic Library
“The concert flute is an edge-tone instrument and consists of three pieces of tubing: the headjoint, middle joint (body) and footjoint. The lip plate and embouchure are set in the conical headjoint. If the embouchure is set on a little plateau it is known as a reform embouchure. This slight elevation facilitates attack, which makes it especially popular with beginners. The upper end of the headjoint is closed by the stopper, which is movable and enables slight adjustments to intonation.”
Flute: Beginner Guide — Music & Arts
“The flute is made up of three parts: The headjoint, body and foot. When connecting the pieces, the hole in the headjoint should line up in a straight line with the row of keys on the body. The main rod on the body of the flute should line up with the middle of the keys on the foot joint.”